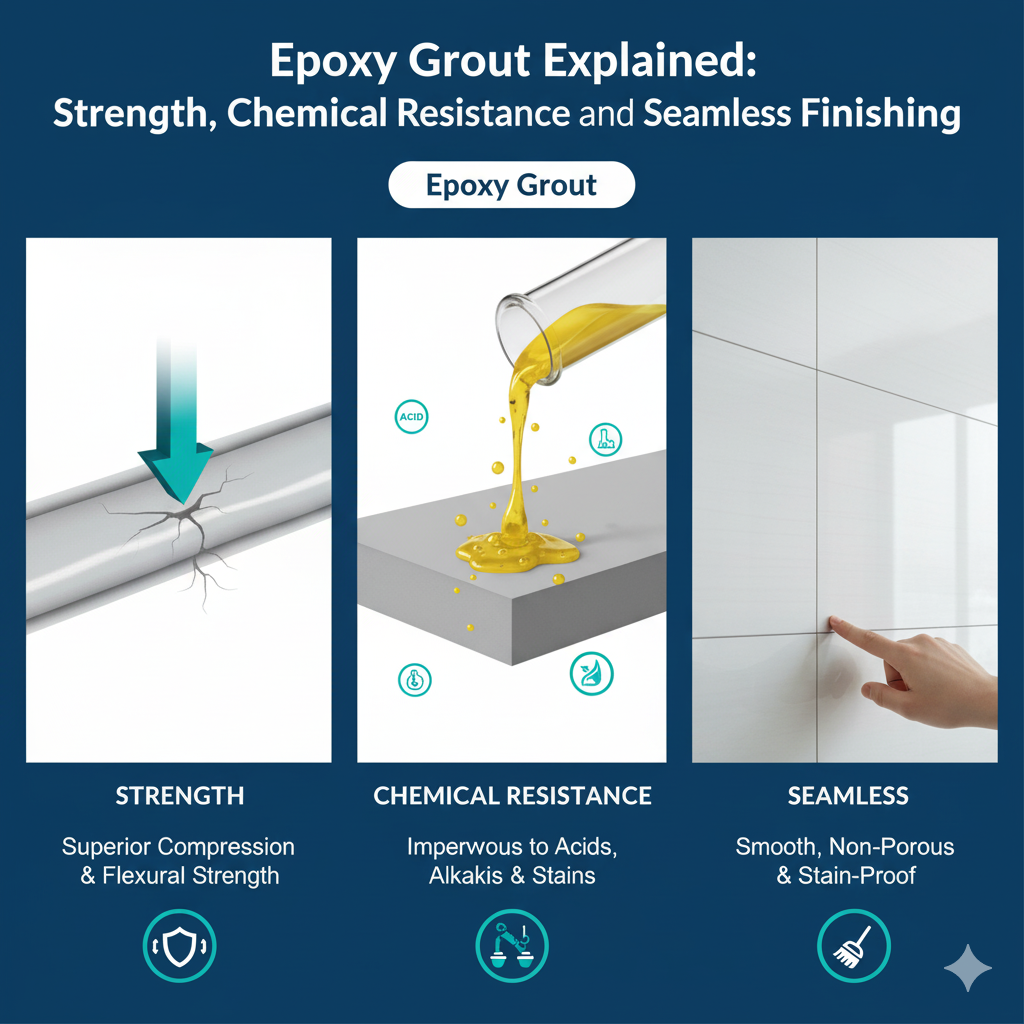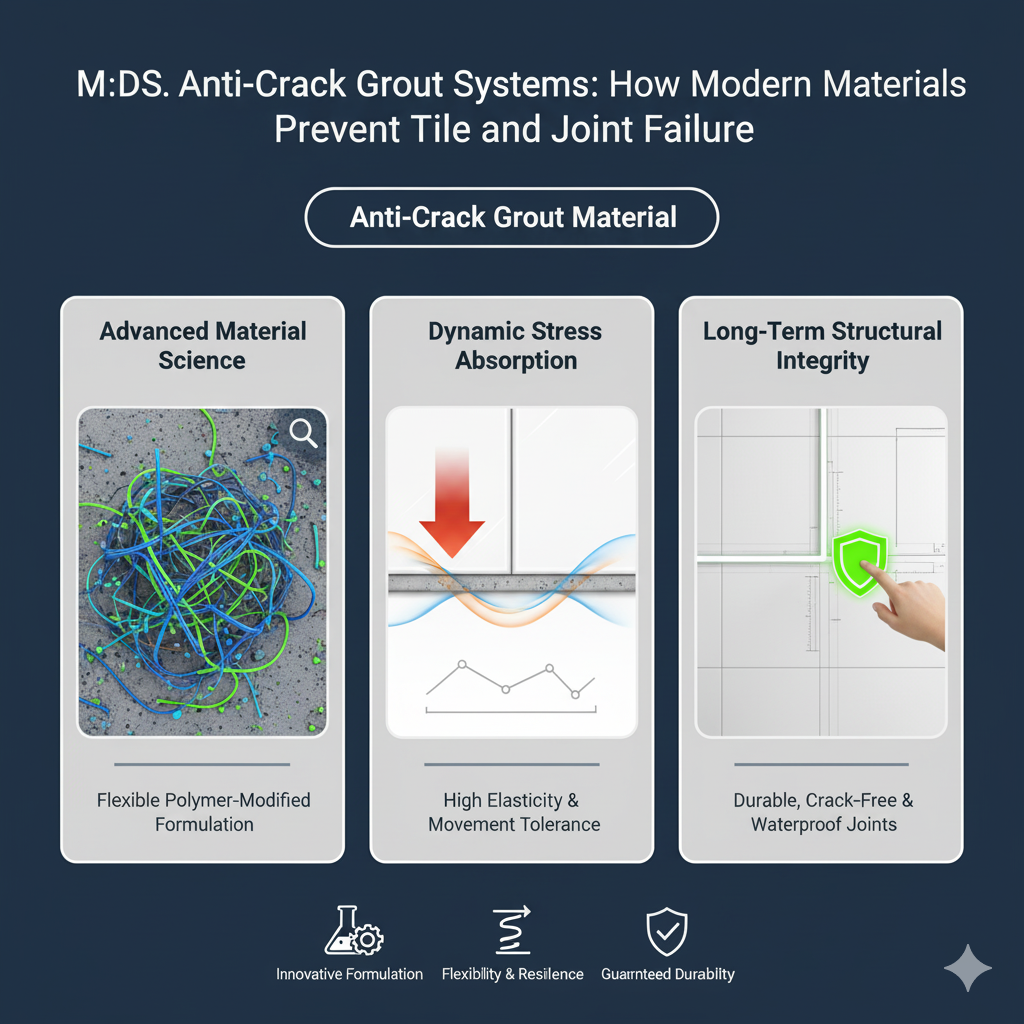
Anti-Crack Grout Systems: How Modern Materials Prevent Tile and Joint Failure
Tile cracks don’t start on the surface—they begin deep within the grout lines. As buildings expand, contract, and shift with temperature or load, traditional grout—rigid and brittle—cannot keep up. The result? Hairline cracks, hollow joints, and ultimately tile detachment.
This is why modern architects and contractors turn to anti-crack grout materials, designed not just to fill space but to absorb movement and maintain stability across the tile assembly.
Factories like YUNYAN have redefined grout composition, replacing purely mineral binders with flexible polymers that adapt to modern building dynamics.
1. Why Cracks Happen in Tile Joints
Cracks occur when internal stress exceeds the elasticity of the grout layer. Common causes include:
-
Substrate movement from temperature or structural settlement
-
Thermal expansion of large-format tiles
-
Improper adhesive coverage leading to uneven support
-
Rapid drying or curing causing shrinkage
-
Heavy loads or impact on floor installations
In each case, rigid grout transfers stress rather than absorbing it—eventually fracturing under tension.
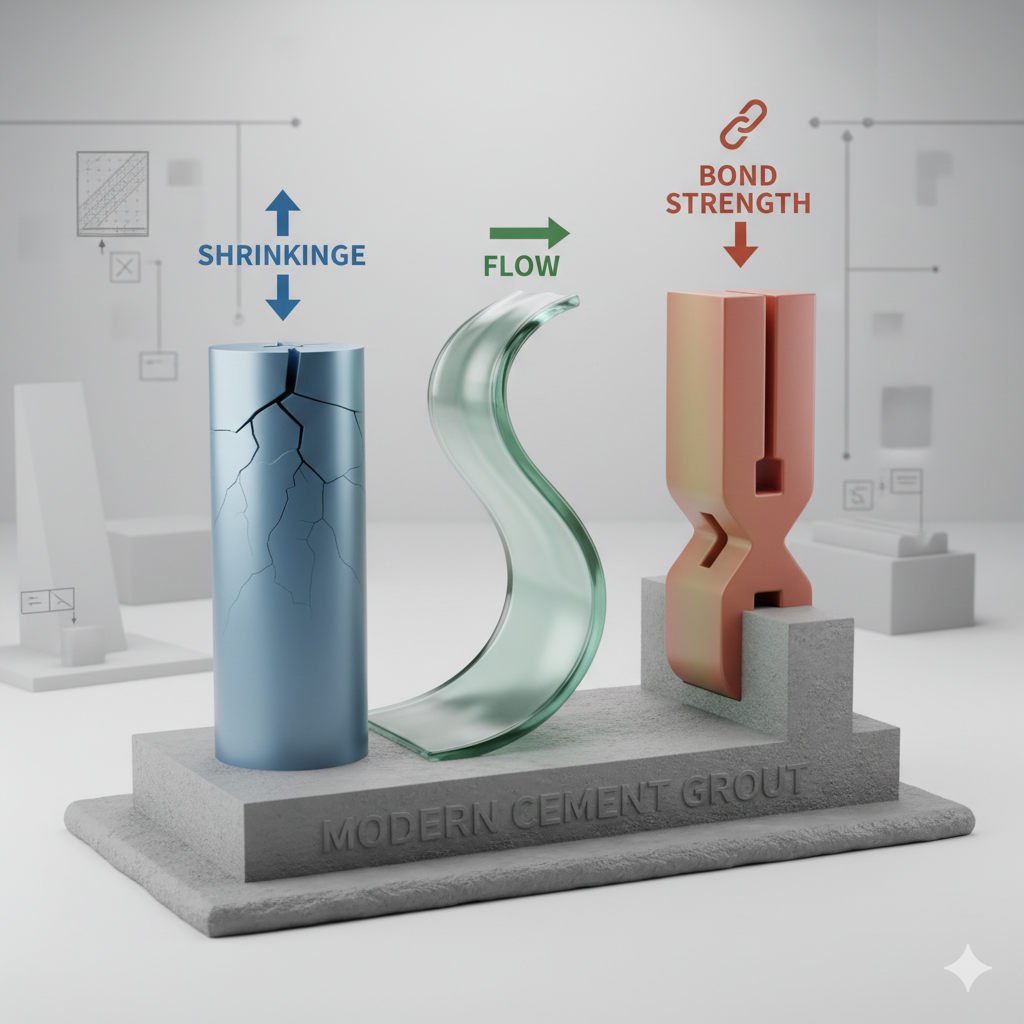
2. The Material Science Behind Anti-Crack Grout
Anti-crack grout materials rely on a balance of flexibility, adhesion, and dimensional stability. Their performance depends on how polymers, fillers, and binders interact during curing.
Core Composition
| Component | Function | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Redispersible Polymer (RDP) | Flexibility and elongation | Absorbs thermal and structural movement |
| Modified Cement Binder | Strength and stability | Prevents micro-fractures |
| Fine Silica Fillers | Dense packing | Reduces voids and shrinkage |
| Shrinkage Compensators | Volume retention | No contraction on curing |
| Latex or Epoxy Additives | Elastic reinforcement | Increases deformability (S1/S2 grade) |
Together, these ingredients create a semi-flexible matrix—rigid enough to support load yet elastic enough to absorb building movement.
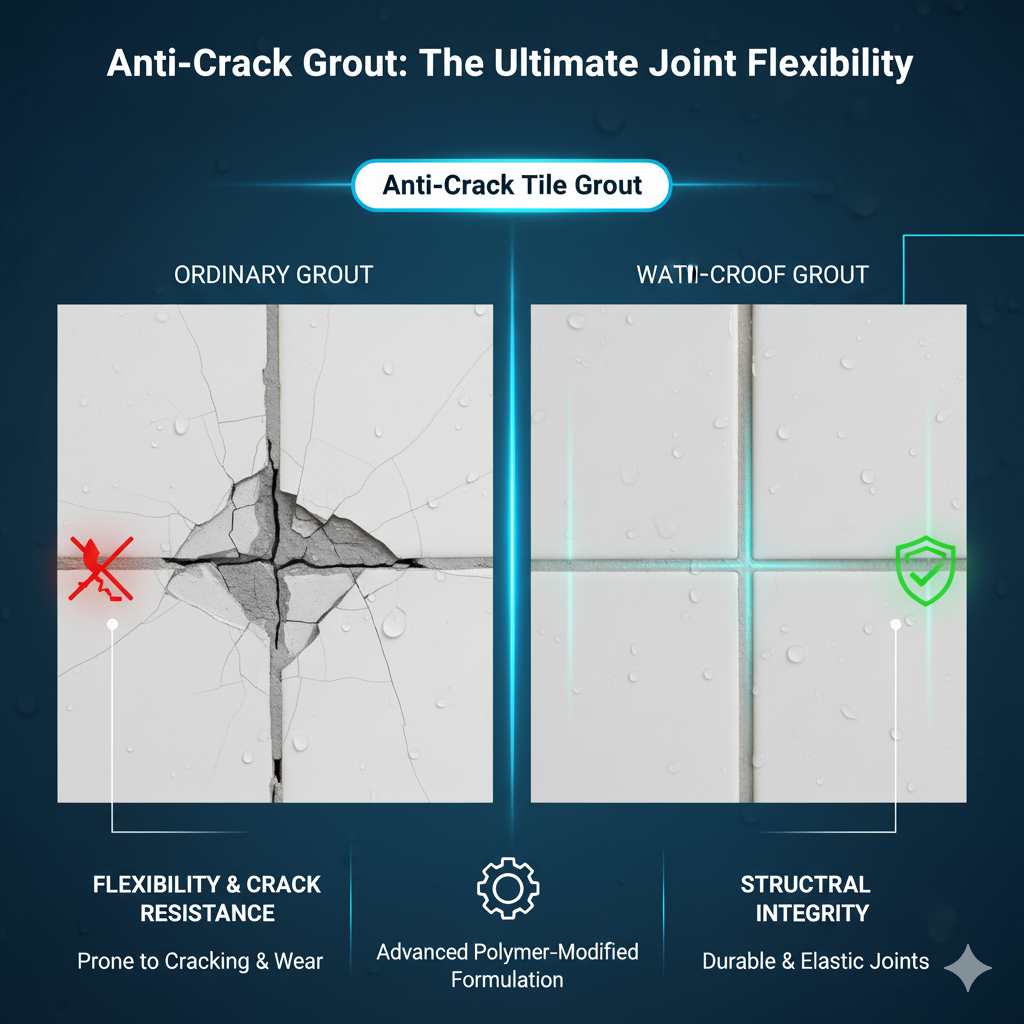
3. How Anti-Crack Grout Performs Compared to Standard Grout
| Property | Standard Grout | Anti-Crack Grout |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Crack Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Shrinkage | Moderate | Compensated |
| Adhesion Strength | Medium | High |
| Thermal Stability | Low | Enhanced |
| Movement Absorption | Minimal | Up to 5 mm lateral |
| Suitable for Large Tiles | ❌ No | ✔ Yes |
While traditional grout focuses on compressive strength, anti-crack grout prioritizes tensile and flexural strength, which directly correlates with crack resistance and lifespan.
4. Factory Engineering: Where Flexibility Is Built
Producing an anti-crack grout material requires precision beyond normal cement blending. A professional supplier controls several variables during manufacturing:
-
Polymer Dispersion Consistency: Ensures homogeneous elasticity across the batch.
-
Moisture-Controlled Storage: Prevents premature polymer degradation.
-
Precision Sieving: Maintains filler uniformity for even curing.
-
Dynamic Mixing Systems: Blend cement, silica, and polymer without segregation.
-
Post-Curing Testing: Simulates real-world expansion cycles and vibration exposure.
Factories like YUNYAN integrate these checks in every production stage to ensure each bag behaves identically—critical for flooring and façade applications across climates.
5. Where Anti-Crack Grout Excels
Large-Format Tiles
Thermal expansion can easily cause joint stress in tiles over 600 mm. Flexible grout absorbs strain without visible cracking.
Balconies and Outdoor Areas
Constant heating and cooling cycles require materials with high deformability and UV resistance.
High-Traffic Commercial Floors
Shops, airports, and stations face mechanical stress from trolleys and cleaning machines—anti-crack grout resists abrasion and impact.
Renovation Projects (Tile-Over-Tile)
The movement of old substrates can cause premature cracking; deformable grout bridges the interface safely.
6. Choosing the Right Anti-Crack Grout System
When evaluating products, don’t just look for “flexible” on the label—check the performance classification.
| Grade | Typical Application | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
| C2 (Basic Polymer) | Standard interior floors | Moderate |
| C2S1 | Large tiles, warm areas | High |
| C2S2 | Exterior façades, extreme climates | Maximum deformability |
Also consider curing speed, water absorption rate, and color stability—especially for outdoor or decorative finishes.
7. The Future of Crack-Free Surfaces
The next generation of anti-crack grout materials is focusing on micro-elastic bonding networks—chemistry that can recover shape even after stress. Combined with low VOC polymers, these materials are also moving toward sustainability while maintaining performance.
As architectural design moves toward larger tiles and thinner joints, flexibility has become as important as strength.
That’s why structural engineers now specify anti-crack grout as part of the tile system, not as a finishing product.
Engineered to Move With the Building, Not Against It
Grout isn’t supposed to break—it’s supposed to adapt. Anti-crack grout materials redefine durability through controlled elasticity, ensuring tiles stay bonded, joints stay intact, and aesthetics stay flawless.
For technical data sheets, performance reports, or custom formulation support, visit YUNYAN’s homepage.
For procurement or OEM cooperation inquiries, reach out via the contact page to connect directly with the materials engineering team.
Crack resistance is no longer optional—it’s the new foundation of reliable tile construction.